Implementing a CRM System in Your Company – How to Do It Right

Modern business is a race for the customer – fast-paced, dynamic, and driven by precise data. Companies that want to manage customer relationships effectively can no longer rely on spreadsheets or scattered email notes. This is where a CRM system steps in, helping to organize workflows, boost team efficiency, and deliver measurable benefits such as improved customer service and increased sales.
But implementing a CRM system isn’t just about choosing the right software – it’s a strategic process that requires preparation, team involvement, and adaptation to the company’s specific needs. So how should you approach it? What are the key stages of CRM implementation? You’ll find the answers in this article.
What Is a CRM System and Why Should You Implement One?
Regardless of industry or company size, building strong customer relationships is essential for long-term success. Without the right CRM tools, however, it becomes difficult to track customer interactions, manage data effectively, or respond in a timely and personalized way. That’s where a CRM platform comes in.
Short for Customer Relationship Management (CRM), this type of solution helps businesses organize, automate, and synchronize their efforts across sales, marketing, and customer service. By equipping your sales team with a well-integrated CRM, you improve internal workflows, increase customer satisfaction, and lay the foundation for stronger customer loyalty.

Definition and Key Features of a CRM System
A CRM system is software that enables companies to manage customer relationships in an organized and automated way. Its main purpose is to streamline the work of sales, marketing, and customer service teams by centralizing information and automating key business processes.
The core features of a CRM system include:
- Customer database management – all customer information and contact history stored in one place,
- Automation of sales and marketing activities,
- Sales funnel monitoring and revenue forecasting,
- Integration with other tools such as email marketing platforms, ERP systems, or e-commerce solutions,
- Analytics and reporting, which support better business decision-making.

What Are the Benefits of Implementing a CRM System?
Implementing a CRM system brings numerous benefits to an organization. Companies that successfully deploy the right CRM solution often see increased sales, improved customer service, and greater operational efficiency.
The key advantages of CRM implementation include:
- Improved workflow organization – the team has quick access to all customer information,
- Increased work efficiency – automation of many manual tasks saves valuable time,
- Better customer service – access to interaction history enables more personalized communication,
- Easier data analysis – the system generates reports that support informed decision-making,
- Integration with other tools – the CRM connects with accounting systems, email platforms, and project management apps.

Thanks to these features, a CRM system becomes more than just a tool that simplifies daily tasks — it turns into a strategic solution that supports business growth and scalability.
CRM Implementation Process – Where to Start?
Deciding to implement a CRM system is only the first step. To ensure the process is successful, proper preparation is essential. Organizational chaos, lack of team engagement, or choosing a system that doesn’t match your company’s needs are common mistakes that can prevent the investment from delivering expected results.
CRM implementation should be treated as a strategic project that requires a well-thought-out approach. Experts recommend focusing on three key initial stages:
- Analyzing business needs,
- Choosing the right CRM system,
- Defining implementation goals.
Each of these steps directly affects the success of the entire initiative, which is why they deserve special attention.
Analyzing Business Needs and Choosing the Right CRM
A CRM implementation should never start with selecting a tool — it should begin with a thorough pre-implementation analysis. One of the most common mistakes companies make is purchasing software before clearly defining which processes they want to optimize and which features are truly necessary.
How to conduct a pre-implementation analysis?
Before choosing a CRM system, it’s worth answering a few essential questions:
- What are the biggest challenges in managing customer relationships? (e.g. lack of contact history, reporting issues, no automation)
- Which business processes need improvement?
- Which departments will use the CRM? (sales, marketing, customer service, finance)
- Will integration with other tools be required? (e.g. ERP, invoicing systems, marketing automation platforms)
- What is the budget for implementing a CRM system?
A well-executed analysis not only helps you better understand your organization’s needs but also prevents unnecessary costs associated with choosing the wrong system.
Defining CRM Implementation Goals
After analyzing your needs, it’s time to clarify what your company aims to achieve with a CRM implementation. One of the main reasons CRM projects fail is the lack of clearly defined objectives.
What goals can be set before implementing a CRM system?
Every organization has different priorities, but the most common CRM implementation goals include:
- Increasing sales efficiency – shortening the sales cycle, improving sales reps’ organization, and closing deals more effectively,
- Better customer data management – centralized client records, full interaction history, segmentation, and personalized engagement,
- Improving customer service quality – faster response times, satisfaction tracking, and automated support processes,
- Optimizing business processes – eliminating unnecessary steps, integrating with other systems, and automating report generation,
- Easier reporting and analytics – real-time sales performance tracking, sales funnel analysis, and identifying the most profitable customers.
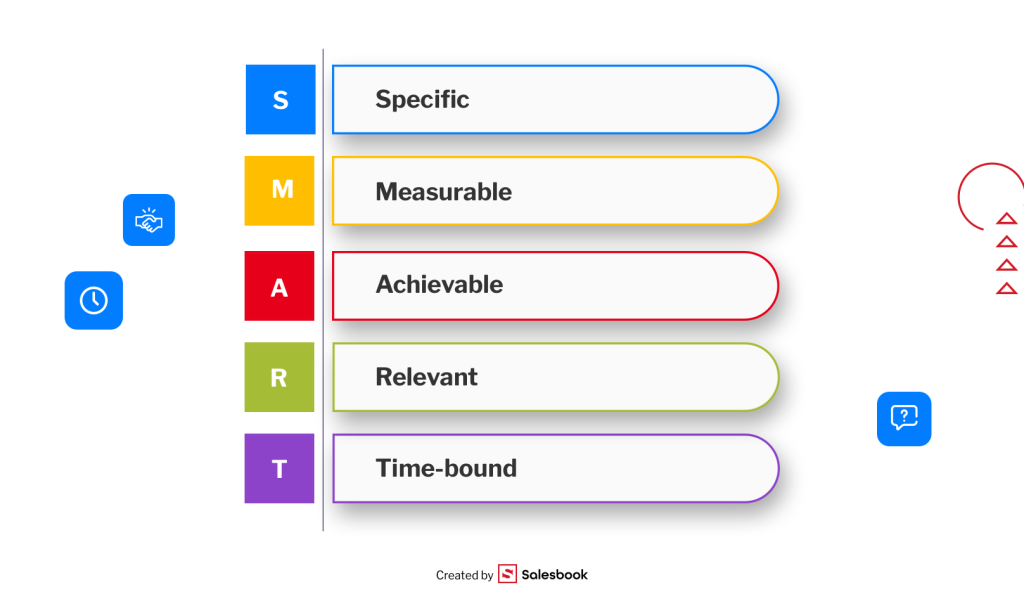
Using the SMART Method to Set CRM Goals
To make your goals effective, apply the SMART framework. Each objective should be:
- S (Specific) – clearly defined (e.g., “Increase the number of closed deals by 20% within six months”),
- M (Measurable) – trackable (e.g., “Improve customer retention rate from 70% to 85%”),
- A (Achievable) – realistic and aligned with your team’s capacity,
- R (Relevant) – directly linked to business priorities,
- T (Time-bound) – with a clear deadline.
This approach allows the company to accurately track progress and assess whether the CRM implementation is delivering the expected results.
What Should You Pay Special Attention To?
When selecting a CRM system, it’s important to focus on the following aspects:
- Ease of use – will the implementation team and employees quickly learn how to use the tool?
- Functionality – does the system meet all key business requirements?
- Customization options – can the CRM be tailored to your organization’s unique needs?
- CRM implementation cost – does the price include employee training, data migration, and technical support?
- Integration with other tools – does the CRM allow for synchronization with your existing IT infrastructure?
According to a Nucleus Research report, companies that implemented modern CRM systems reported an average return on investment (ROI) of $8.71 for every dollar spent (source). This shows how significant the impact of a well-chosen tool can be.
CRM Implementation Stages – How to Roll It Out Successfully?
Implementing a CRM system in your company requires a structured approach and a well-planned strategy. It’s not just about selecting the right software – it’s also about executing each phase of the rollout effectively. Mistakes made during this process can lead to low employee adoption and even complete failure of the implementation.
So how can you ensure a smooth and successful process? Below are the key CRM implementation stages that will help your deployment run efficiently and deliver the expected results.
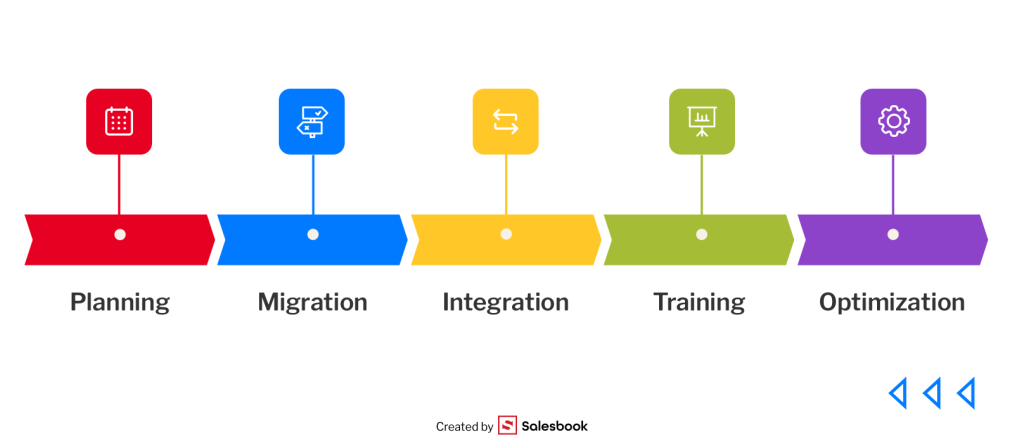
Stage 1: Planning and Preparing for Implementation
Every successful CRM implementation begins with a solid plan. This stage includes developing an implementation timeline, defining roles and responsibilities, and preparing the organization for the upcoming change.
1. Creating an Implementation Team
A crucial step is forming an implementation team responsible for overseeing the entire process. This team should include representatives from key departments such as sales, marketing, customer service, and IT. Each of them brings a unique perspective, which helps tailor the system to the organization’s real needs.
2. Developing an Implementation Timeline
The CRM rollout plan should include clearly defined steps and a schedule. It’s important to incorporate the following elements:
- System configuration and customization,
- Data migration,
- Integration of the CRM with other tools,
- Team training,
- System testing and adjustments,
- Full system launch.
Example:
When implementing a CRM in a trading company, it’s essential to test automated sales reports, as this is one of the core business processes in that industry. In Salesbook, users can quickly generate team performance analyses, allowing for more effective sales management.

3. System Setup and CRM Customization
Every company has its own unique processes, which is why CRM setup should include configuration tailored to the specific nature of the business. At this stage, you define:
- Data structures and contact categories,
- Automatic lead assignment to sales reps,
- Sales paths and funnel stages,
- Notifications and tasks assigned to users.
According to Gartner experts, companies that customize their CRM to match internal workflows see up to 20% higher user adoption among employees.
Stage 2: Migrating Data to the CRM System
One of the most demanding stages of implementation is data migration — transferring information from legacy systems (e.g., spreadsheets, old CRM databases, ERP systems) to the new platform. This is a critical moment that determines the quality and usability of the system.
1. Pre-Migration Data Audit
Before transferring data to the new CRM, it’s important to conduct a data audit to check:
- Are the records current and accurate?
- Are there any duplicates?
- Do they include all key information (e.g., interaction history, notes, segmentation)?
2. Data Migration Methods
There are several ways to migrate data:
- Manual import – suitable for smaller datasets, e.g., via spreadsheets,
- Automated migration – using APIs or dedicated integration tools,
- Staged migration – transferring data in batches to minimize errors and maintain operational continuity.
Example:
A company using multiple sales systems simultaneously can benefit from automated data migration to synchronize contact databases in the new CRM. Salesbook offers integrations with popular sales tools, significantly speeding up this process.
3. Testing Data Migration Accuracy
After transferring the data, it is essential to review and verify its integrity. This should include:
- Testing for data accuracy and consistency,
- Checking whether the system correctly assigns leads and interaction history,
- Evaluating the clarity and organization of data in the new environment.
Companies that skip post-migration testing often face missing information and disruptions in the daily operations of their sales teams.
Stage 3: Integrating the CRM with Other Tools
Modern CRM software rarely operates in isolation. Integrating the CRM with the tools your company uses daily increases process efficiency and prevents duplicated work.
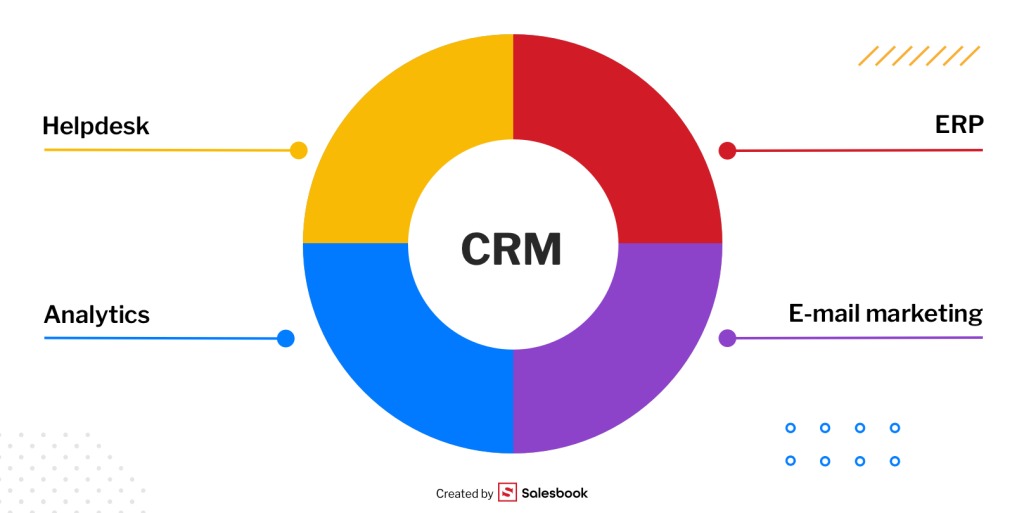
1. Which Systems Should Be Integrated with Your CRM?
- ERP systems – syncing the CRM with your accounting system enables automatic invoice generation and payment tracking,
- Email marketing platforms – integration allows for running email campaigns and automatically updating your subscriber database,
- Analytics tools – connecting your CRM to BI platforms (e.g., Power BI) provides deeper insights into sales data,
- Customer support systems – a CRM integrated with a helpdesk system lets you track the full history of customer tickets,
- Workflow automation tools – integrating with task management tools like ClickUp or Trello enables real-time monitoring of business processes in one centralized place.
2. Using APIs for Integration
Modern CRM systems offer integration capabilities through APIs, allowing data flows to be tailored to the specific needs of the organization. In Salesbook, the API enables synchronization between the CRM and internal sales and marketing systems, making it possible to fully automate key processes.
3. Testing and Optimizing Integrations
After integration is implemented, it’s important to regularly test its functionality and assess the outcomes. Key questions to ask include:
- Are data flows between systems error-free?
- Are automations working as intended?
- Are employees using the new features effectively?
A well-executed data migration and successful CRM integration with other tools form the foundation of a smooth and effective implementation.
Common Mistakes in CRM Implementation and How to Avoid Them
Implementing a CRM system can significantly improve customer relationship management — but only if done correctly. Unfortunately, many companies make mistakes that result in low user adoption, failure to achieve expected benefits, or even complete project failure.
Below are the most common pitfalls and strategies for avoiding them.

1. Lack of Clearly Defined Implementation Goals
Many companies move forward with CRM implementation without precisely defining what they want to achieve. Without clear goals, the system may be poorly configured, fail to meet user expectations, and ultimately bring little to no business value.
How to avoid it:
- Apply the SMART method when setting goals, e.g., “Increase the number of closed deals by 20% within six months.”
- Identify specific business processes the CRM should improve, such as reporting automation, customer segmentation, or reducing response time to inquiries.
- Regularly review whether the system is meeting its objectives and adjust configurations as needed.
2. Choosing the Wrong CRM System
The market offers a wide range of CRM systems — from simple contact management tools to advanced analytics platforms. Not every company needs the same set of features.
How to avoid it:
- Analyze your company’s needs and create a list of key requirements before making a final decision.
- Choose a CRM system that fits the size and workflows of your organization.
- Test the system before purchasing — most providers offer demo versions.
- Consider the CRM’s ability to integrate with other tools already used in your company.
Example:
Companies in the trade sector can benefit from a CRM system that offers interactive sales tools and real-time reporting. Salesbook provides exactly these kinds of solutions, helping sales teams respond quickly to customer needs and improve their closing rates.
3. Skipping Data Analysis Before Migration
Companies often transfer outdated, incomplete, or duplicate customer data into the new system, which creates confusion and makes the CRM harder to use.
How to avoid it:
- Conduct a data audit before migration to remove outdated entries and eliminate duplicates.
- Create a consistent data structure to keep information organized.
- Run a test migration with a small sample of data to identify potential issues before full deployment.
4. Lack of Team Involvement and Resistance to Change
CRM is designed to help employees — yet it often meets resistance. The reasons vary: lack of knowledge, fear of complex systems, or habits tied to old workflows.
How to avoid it:
- Involve employees in the selection and implementation process.
- Organize team training to ensure users know how to work efficiently with the new system.
- Highlight specific benefits for staff — such as automation of time-consuming tasks or easier access to customer data.
5. Lack of Post-Implementation Optimization
Many companies treat CRM implementation as a one-time project and fail to monitor its performance over the long term. In reality, the system requires ongoing optimization to stay effective.
How to avoid it:
- Regularly evaluate whether the CRM continues to meet your business goals.
- Gather user feedback and make adjustments to the system configuration.
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as response time to customer inquiries or deal closure rates.
Summary – How to Successfully Implement a CRM System
A successful CRM implementation is a process that requires a thoughtful approach and commitment from the entire organization. Whether you’re adopting CRM software for the first time or replacing an existing solution, it’s crucial to go through all the key stages in a structured manner.
What steps guarantee a successful CRM implementation?
- Conducting a pre-implementation analysis
- Define your company’s needs and the key areas where CRM should improve performance.
- Determining the required functionality
- Identify what features the best CRM system should offer for your organization.
- Selecting the right system and vendor
- Evaluate the cost and features of various systems.
- Determine how much CRM implementation will cost and whether it includes technical support and customization.
- Preparing for data migration
- Audit and clean your data before transfer.
- Define the customer database structure and contact segmentation.
- Training your team and providing learning resources
- Organizational change requires the right employee onboarding strategy.
- Offering comprehensive training materials increases system adoption.
- Integrating the CRM with other tools
- Connect your CRM with accounting systems, marketing automation tools, or sales platforms.
- Automate data flows between different departments.
- Monitoring and optimizing performance
- Continuously analyze the system’s effectiveness.
- Adjust workflows and settings based on user feedback.

Discover Salesbook CRM
If you’re looking for a solution that not only streamlines sales but also simplifies customer relationship management, take a closer look at Salesbook CRM. It’s a tool designed for modern businesses that want to fully unlock their team’s potential.
Learn more and try Salesbook CRM today.
Table of Contents







